Building decarbonization refers to strategies, initiatives, and measures that aim to reduce the greenhouse gas emissions (“GHG”) of buildings throughout their lifecycles.
This can be viewed from several different stakeholder lenses, including infrastructure ownership or utility investment, real estate asset ownership or an occupant perspective. The main purpose of this paper is to highlight the growing infrastructure investment opportunity for building decarbonization strategies in the U.S.
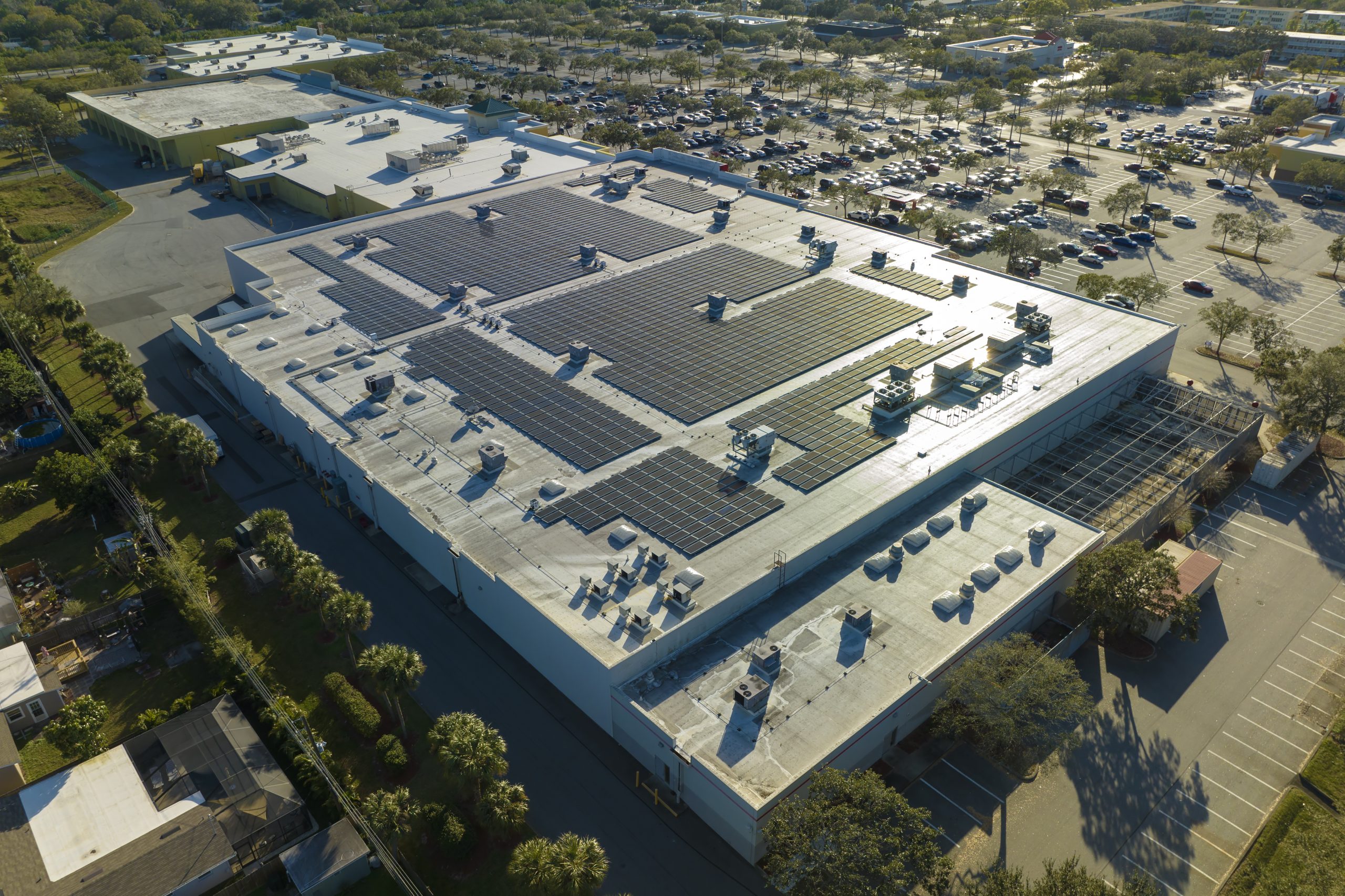
Building decarbonization can be achieved in various ways, including implementing energy efficiency measures, deploying renewable energy infrastructure, building electrification, on-site energy generation and storage, utilizing low carbon construction materials, and incorporating building automation, monitoring, and optimization.
Measures can be applied to both new developments and existing assets and, as described in more detail herein, the initiatives to achieve decarbonization typically fall into one or more of the following categories:
- ENERGY USE REDUCTION — Investments both upfront (e.g., the use of low carbon construction materials) and ongoing (e.g., upgrading existing equipment to more efficient technologies) that reduce the baseline energy consumption needs of a building.
- A “GREENING” OF EXISTING ENERGY USAGE — transitioning the energy sources of a building towards a greener and less carbon intensive energy mix (e.g., on-site renewable energy generation).
- A OPTIMIZATION OF ENERGY USAGE — enabling buildings to manage the energy that must be consumed, in the most efficient and optimal manner (e.g., smart building controls and demand response).